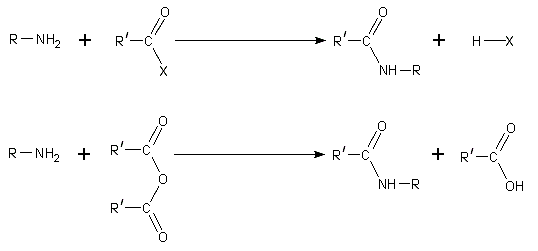
The dominant reactivity of amines is their nucleophilicity. Most primary amines are good ligands for metal ions to give coordination complexes. Amines are alkylated by alkyl halides. Acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides react with primary and secondary amines to form amides (the "Schotten-Baumann reaction").
Similarly, with sulfonyl chlorides, one obtains sulfonamides. This transformation, known as the Hinsberg reaction, is a chemical test for the presence of amines.
Because amines are basic, they neutralize acids to form the corresponding ammonium salts R3NH+. When formed from carboxylic acids and primary and secondary amines, these salts thermally dehydrate to form the corresponding amides.
Amines react with nitrous acid to give diazonium salts. The alkyl diazonium salts spontaneously decompose by losing N2 to produce a mixture of alkenes, alkanols or alkyl halides, with alkanols as the major product. This reaction is of little synthetic importance because the diazonium salt formed is too unstable.

Primary aromatic amines, such as aniline ("phenylamine") form more stable diazonium salts, which can be isolated in the crystalline form. These species undergo a variety of synthetically useful transformations. With cuprous cyanide the corresponding nitrile is formed. Arenediazonium ions undergo coupling with electron-rich aromatic compounds such as a phenol to form an azo compound. These species are widely used as dyes.

Imine formation is an important reaction. Primary amines react with ketones and aldehydes to form imines. In the case of formaldehyde (R' = H), these products typically exist as cyclic trimers.
- RNH2 + R'2C=O → R'2C=NR + H2O
Reduction of the imines gives secondary amines:
- R'2C=NR + H2 → R'2CH-NHR
Similarly, secondary amines react with ketones and aldehydes to form enamines:
- R2NH + R'(R"CH2)C=O → R"CH=C(NR2)R' + H2O
An amine reaction overview is given below:
Reaction name  | Reaction product  | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Amine alkylation | amines | degree of substitution increases |
| Schotten-Baumann reaction | amides | Reagents: acyl chlorides, acid anhydrides |
| Hinsberg reaction | sulfonamides | Reagents: sulfonyl chlorides |
| Amine-carbonyl condensation | imines | |
| Organic oxidation | nitroso compounds | Reagent: peroxymonosulfuric acid |
| Organic oxidation | diazonium salt | Reagent: nitrous acid |
| Zincke reaction | Zincke aldehyde | reagent pyridinium salts , with primary and secondary amines |
| Emde degradation | tertiary amine | reduction of quaternary ammonium cations |
| Hofmann-Martius rearrangement | aryl substituted anilines | |
| Von Braun reaction | Organocyanamide | By cleavage (tertiary amines only) with cyanogen bromide |
No comments:
Post a Comment